• PreparedStatement is an interface available in java.sql package and extends Statement interface.
• You can create the PreparedStatement using the following methods of Connection interface.
○ public PreparedStatement prepareStatement(sql)
○ public PreparedStatement prepareStatement(sql,int , int)
○ public PreparedStatement prepareStatement(sql,int ,int ,int)
• After creating the PreparedStatement object , you can call one of the following methods to submit the SQL Statement to Database.
○ public int executeUpdate()
○ public boolean execute()
○ public ResultSet executeQuery()
• Using a PreparedStatement type object, you can submit only one SQL statement.
Example :-
String sql="insert ....";
PreparedStatement ps=con.prepareStatement(sql)
int x=ps.executeUpdate();

• When you submit the SQL Statement using PreparedStatement object then SQL Statement will be compiled only once at first time and pre-compile SQL Statement will be executed every time.
Total time = req.time + compile time + exec time + res.time = 5 ms+5 ms+5 ms+5 ms = 20 ms.
First time -> 1 SQL Stmt = 20 ms.
Next onwards -> 5ms + 0 ms+ 5 ms +5 ms= 15 ms.
101 times = 20 ms + 1500ms.=> 1520 ms.
• PreparedStatement gives you the place holder mechanism for providing the data dynamic to the query.You need to use ? Symbol for placeholder.
• To provide the value of place holder you need to invoke the following method:
public void setX(int paramIndex, X val)
X can be int,String,long,float,Date etc
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.Statement;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Jtc5 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/tutorial";
Connection con = DriverManager.getConnection(url, "root", "root");
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
String sql = "insert into JtcStudent values (?,?,?,?)";
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = con.prepareStatement(sql);
for (int i = 1; i <= 3; i++) {
System.out.println("Enter Student Id :- ");
int sid = scanner.nextInt();
scanner.nextLine();
System.out.println("Enter Student Name :- ");
String sname = scanner.nextLine();
System.out.println("Enter Student Email :- ");
String semail = scanner.nextLine();
System.out.println("Enter Student City :- ");
String scity = scanner.nextLine();
preparedStatement.setInt(1, sid);
preparedStatement.setString(2, sname);
preparedStatement.setString(3, semail);
preparedStatement.setString(4, scity);
int j = preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
if (j == 1) {
System.out.println("Record Inserted...");
}
System.out.println("---------------");
}
}
}
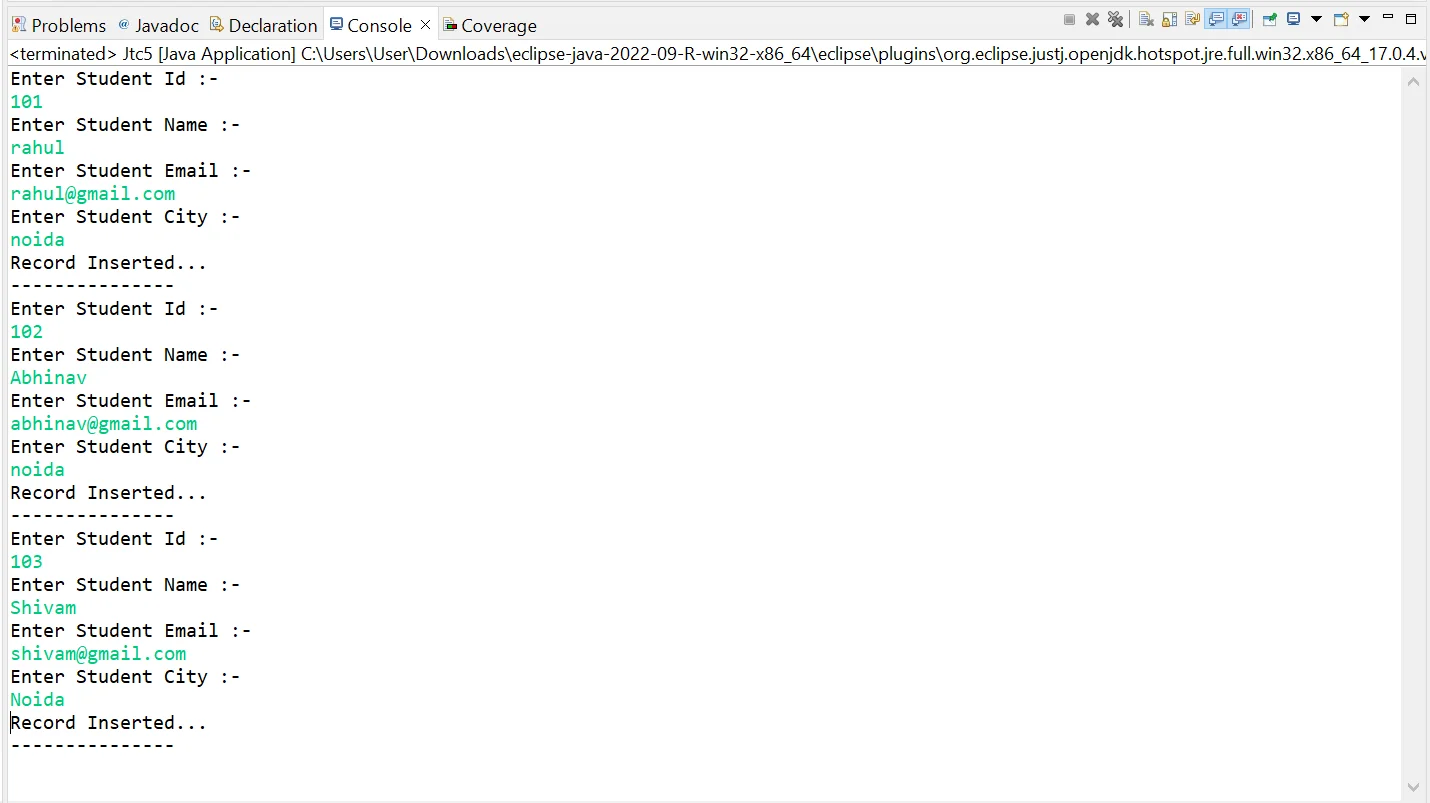
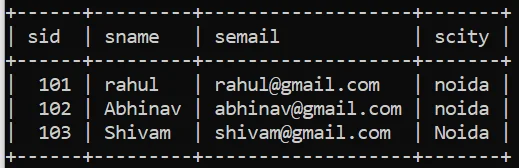
In the above Example we are using java.sql.PreparedStatement type object to submit SQL query to the database.
As we discussed using an object of java.sql.PreparedStetement type object we can submit only one query, the same concept we can see into the above example.
String sql = "insert into Student values (?,?,?)";;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = con.prepareStatement(sql);
And then after we are using Placeholder mechanism to set the dynamic value to the SQL query along with different setter methods.
preparedStatement.setInt(1, sid);
preparedStatement.setString(2, sname);
preparedStatement.setString(3, scity);
And finally submit the SQL query to the Database.