New Features added in JDBC4.0
1. Auto-loading of JDBC driver class
2. SQL exception handling enhancements
3. Connection management enhancements
New Features added in JDBC4.1
1. try with resource/ Automatic Resource Management.
2. RowSetFactory Interface and RowSetProvider Class
New Features added in JDBC4.2
1. Addition of REF_CURSOR support
2. Addition of the java.sql.JDBCType Enum
3. Add support for large update counts
Before to JDBC4.0 , you need to get the Connection object as follows:
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
con=DriverManager.getConnection(url,un,pw);
DriverManager.getConnection() method is doing the following tasks:
Takes the URL.
Identifies the Database related to the URL given
Checks whether the Driver class related to given URL is loaded or not.
If loaded then creates the Connection interface sub class object provided by that database vendor.
If not loaded then gives the SQLException with message - No suitable Driver found.
From JDBC4.0 onwards, you need to get the Connection object as follows:
con=DriverManager.getConnection(url,un,pw);
DriverManager.getConnection() method is doing the following tasks:
Takes the URL.
Identifies the Database related to the URL given.
Loads the required driver class automatically when driver class is not loaded (if the driver class is found in application classpath).
Creates the Connection interface sub class object provided by that database vendor.
From JDBC 4.0 onwards, SQLException object is an Iterator which can hold multiple Exception objects raised in JDBC code.
| From JDBC4.0 | From JDBC4.0 |
|---|---|
| try{ ... }catch(SQLException ex){ for(Throwable e:ex){ System.out.println(e); e.printStackTrace(); } } |
try{ ... }catch(SQLException ex){ for(Throwable e:ex){ System.out.println(e); e.printStackTrace(); } } |
You have to use Database vendor provided DataSource class to get the connection object.
For Oracle Database :
OracleDataSource ods = new OracleDataSource();
ods.setURL("jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:XE");
ods.setUser("system");
ods.setPassword("india");
con = ods.getConnection();
Upto Java 6, when you are initializing resources to establish the connection between Java
program and IO Device or DB Engine etc then you must have to close the resources explicitly
using finally block.
From Java 7, new feature added called try-with resources which helps to close or clean the
resources automatically.
Syntax:
try(<Resources Declaration and Initialization>)
{
…
}catch(<throwableType> refVar){
…
}
When a class is implementing java.lang.AutoCloseable interface then only those class objects can be used with try-with resources for auto cleanup.
With try-with resources try block can be used without catch and finally blocks also.
package com.jtcindia.jdbc;
import java.sql.*;
public class tryWithResource {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String URL = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/tutorial?autoReconnect=true&useSSL=false";
String UN = "root";
String PW = "root";
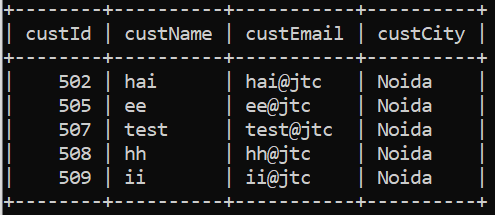
String SQL = "select * from mycustomers ";
try (Connection con = DriverManager.getConnection(URL, UN, PW); Statement st = con.createStatement(); ResultSet rs = st.executeQuery(SQL)) {
while (rs.next()) {
int cid = rs.getInt(1);
String cn = rs.getString(2);
String em = rs.getString(3);
String ci = rs.getString(4);
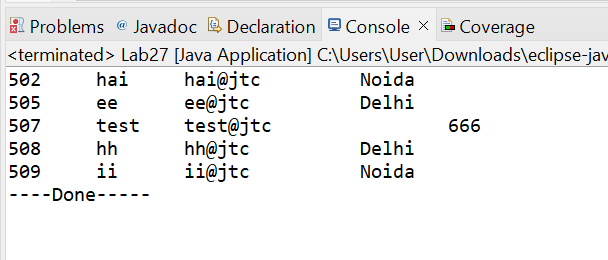
System.out.println(cid + "\t" + cn + "\t" + em + "\t" + "\t" + ci);
}
System.out.println("----Done-----");
} catch (Exception ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}
}

The REF_CURSOR data type is supported by several databases. To return a REF_CURSOR from a stored procedure you can use this type.
To check whether JDBC Driver supports REF_CURSOR you can invoke the supportsRefCursors () method with DatabaseMetaData.
This enum identifies generic SQL Types, called JDBC Types. You can use JDBCType in place of the constants defined in Types.
JDBC methods returns only int value for the update count.
Since datasets continue to grow, this can cause problems.
So following methods are added to the Statement that returns a long value for the update count.
public long getLargeUpdateCount()
public long getLargeMaxRows()
public long[] executeLargeBatch()
public long executeLargeUpdate(java.lang.String)
package com.jtcindia.jdbc;
import java.sql.*;
public class tryWithResource {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String URL = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/tutorial?autoReconnect=true&useSSL=false";
String UN = "root";
String PW = "root";
String SQL = "select * from mycustomers ";
try (Connection con = DriverManager.getConnection(URL, UN, PW); Statement st = con.createStatement(); ResultSet rs = st.executeQuery(SQL)) {
while (rs.next()) {
int cid = rs.getInt(1);
String cn = rs.getString(2);
String em = rs.getString(3);
String ci = rs.getString(4);
System.out.println(cid + "\t" + cn + "\t" + em + "\t" + "\t" + ci);
}
System.out.println("----Done-----");
} catch (Exception ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}
}