When you submit multiple queries to database one by one then lot of time will be wasted for request and response.

Using Statement
For 1 SQL Statement = 5ms +5ms + 5ms + 5ms =20 ms
For 100 SQL Statements = 100 * 20= 2000ms
Using PreparedStatement
For 1 SQL Statement = 5ms +0ms + 5ms + 5ms =15 ms
For 100 SQL Statements = 100 * 15= 1500ms
In the above two cases, you are trying to submit 100 SQL Statements. For submitting 100 SQL Statements, you need to communicate with the database 100 times. This increases number of round trips between your application and database which damages the application performance. Batch updates allows you to submit multiple SQL statements as One Batch to the Database at a time.
Using Batch Updates
For 100 SQL Statements = 5ms +100 * 5ms + 100 * 5ms + 5ms
= 5ms +500ms + 500ms + 5ms
=1010 ms
Using Batch Updates with Statement:
You can submit multiple types of SQL Statements.
You can submit multiple SQL Statements.
You can reduce number of round trips between your application and database
which improves the application performance.
You can use insert, update and delete statements only.
You can not use SELECT statement.
Use the following methods of Statement interface to implement Batch Updates.
void addBatch(String) :
• Adds the given SQL command to the current list of commands for this Statement object. When call executeBatch Method, the commands in this list can be executed as a batch.
• This method cannot be called on a PreparedStatement or CallableStatement.
• Parameters : SQL INSERT or UPDATE statement.
• Throws : SQLException
int [ ] executeBatch() :
• Submits a batch of commands to the database for execution.
• When all commands execute successfully, returns an array of update counts.
• Returns : An array of update counts containing one element for each command in the batch.
• Throws : SQLException, BatchUpdateException (a subclass of SQLException), SQLTimeoutException
void clearBatch() :
• Remove Statement object's current list of SQL commands.
• Throws : SQLException
Using Batch Updates with PreparedStatement:
You can submit only single type of SQL Statement.
You can submit multiple SQL Statements.
You can reduce number of round trips between your application and database
which improves the application performance.
You can use insert, update and delete statements only.
You can not use SELECT statement.
Use the following methods of PreparedStatement interface to implement Batch Updates.
void addBatch() :
• Adds a set of parameters to this PreparedStatement object's batch of commands.
• Throws : SQLException
int [ ] executeBatch() :
• Same method is inheriting from Statement Interface.
void clearParameters() :
• It clears the current parameter values.
• Throws : SQLException.
package com.jtcindia.jdbc;
import java.sql.*;
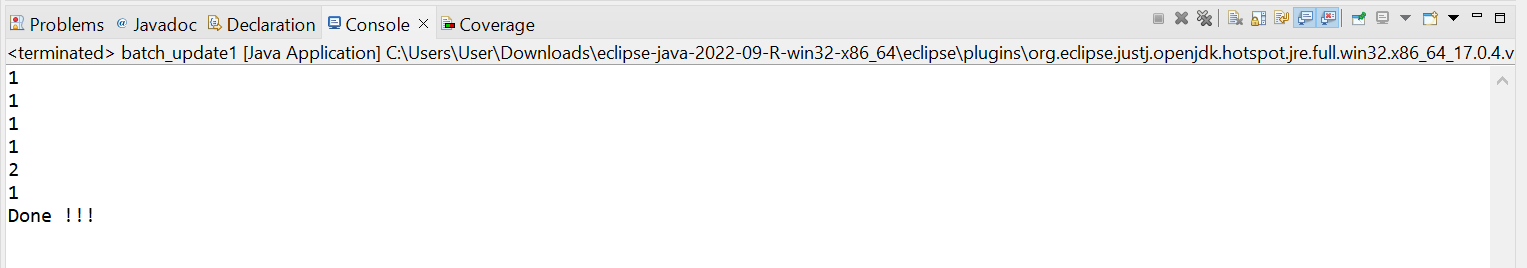
public class batch_update1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException {
Connection con = null;
Statement st = null;
try {
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/tutorial?autoReconnect=true&useSSL=false";
con = DriverManager.getConnection(url, "root", "root");
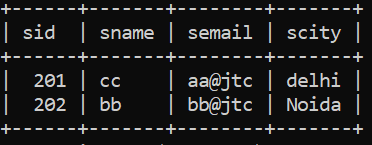
String SQL1 = "insert into JtcStudent values(201,'aa','aa@jtc','Noida')";
String SQL2 = "insert into JtcStudent values(202,'bb','bb@jtc','Noida')";
String SQL3 = "insert into JtcStudent values(203,'cc','cc@jtc','delhi')";
String SQL4 = "update JtcStudent set scity='delhi' where sid=201";
String SQL5 = "update JtcStudent set sname='cc' where scity='delhi'";
String SQL6 = "delete from JtcStudent where sid=203";
st = con.createStatement();
st.addBatch(SQL1);
st.addBatch(SQL2);
st.addBatch(SQL3);
st.addBatch(SQL4);
st.addBatch(SQL5);
st.addBatch(SQL6);
int results[] = st.executeBatch();
for (int x : results) {
System.out.println(x);
}
System.out.println("Done !!! ");
} catch (Exception ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
} finally {
st.close();
con.close();
}
}
}
package com.jtcindia.jdbc;
import java.sql.*;
public class batch_update2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException {
Connection con = null;
PreparedStatement ps = null;
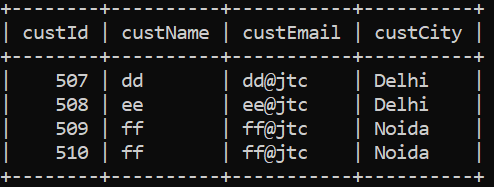
Object[][] mycustomers = {
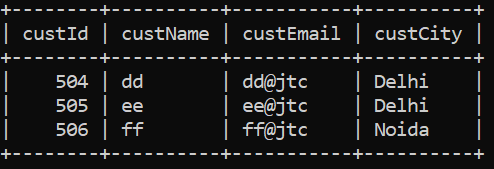
{ 504, "dd", "dd@jtc", "Delhi" },
{ 505, "ee", "ee@jtc", "Delhi" },
{ 506, "ff", "ff@jtc", "Noida" },
};
try {
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/tutorial?autoReconnect=true&useSSL=false";
con = DriverManager.getConnection(url, "root", "root");
String SQL = "insert into mycustomers values(?,?,?,?)";
ps = con.prepareStatement(SQL);
for (Object[] mycust : mycustomers) {
ps.setInt(1, (int) mycust[0]);
ps.setString(2, (String) mycust[1]);
ps.setString(3, (String) mycust[2]);
ps.setString(4, (String) mycust[3]);
ps.addBatch();
}
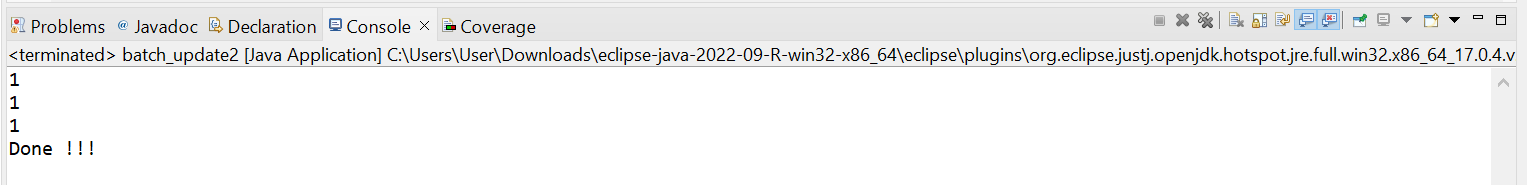
int results[] = ps.executeBatch();
for (int x : results) {
System.out.println(x);
}
System.out.println("Done !!! ");
} catch (Exception ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
} finally {
ps.close();
con.close();
}
}
}
package com.jtcindia.jdbc;
import java.sql.*;
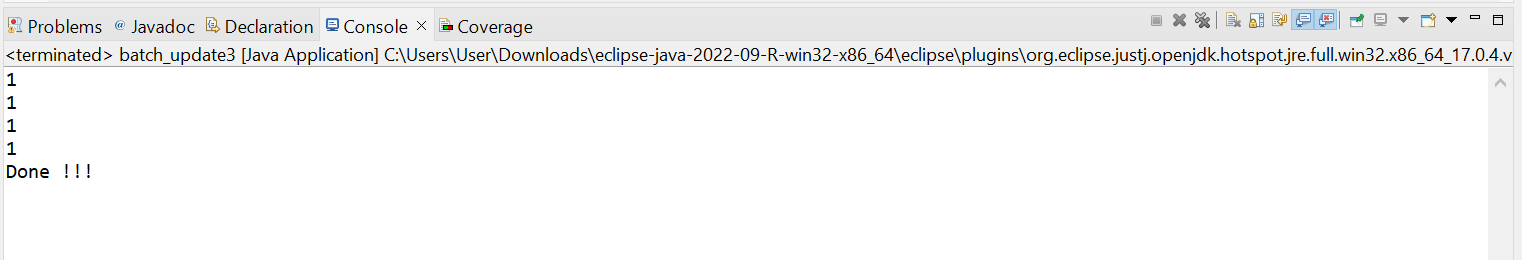
public class batch_update3 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException {
Connection con = null;
PreparedStatement ps = null;
Object[][] mycustomers = {
{ 507, "dd", "dd@jtc", "Delhi" },
{ 508, "ee", "ee@jtc", "Delhi" },
{ 509, "ff", "ff@jtc", "Noida" },
{ 510, "ff", "ff@jtc", "Noida" }, };
try {
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/tutorial?autoReconnect=true&useSSL=false";
con = DriverManager.getConnection(url, "root", "root");
String SQL = "insert into mycustomers values(?,?,?,?)";
ps = con.prepareStatement(SQL);
for (Object[] mycust : mycustomers) {
int paramNum = 1;
for (Object obj : mycust) {
ps.setObject(paramNum++, obj);
}
ps.addBatch();
}
int results[] = ps.executeBatch();
for (int x : results) {
System.out.println(x);
}
System.out.println("Done !!! ");
} catch (Exception ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
} finally {
ps.close();
con.close();
}
}
}